¿Cuál es más contaminante: el diésel o la gasolina?
The debate over which fuel is more polluting, whether diesel or gasoline, has generated various opinions and studies in the present. Both types of fuel have raised concerns about their emissions and their impact on the environment. While diesel has been associated with higher levels of nitrogen oxides and fine particulate matter, gasoline may contribute more significantly to the emission of carbon dioxide (CO2). This analysis delves into the technical and environmental aspects of each to understand their contaminating effects on the atmosphere.
The debate over the pollution caused by diesel and gasoline is relevant in the current context, where sustainability and emission reduction are priority issues. Both diesel and gasoline have their advantages and disadvantages in terms of polluting emissions. In this article, we will examine the effects of each type of fuel on air pollution and its environmental impact.
Composition of Fuels
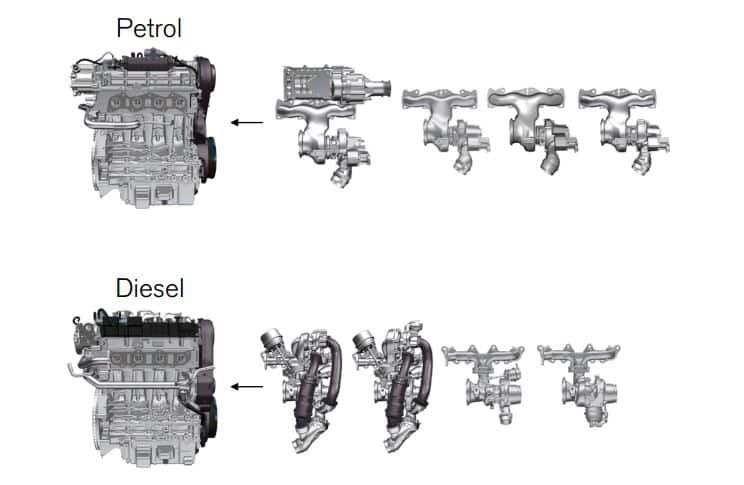
Diesel and gasoline differ not only in their chemical composition but also in how these fuels affect the environment. Gasoline, on one hand, is a more volatile product, while diesel is denser and contains more energy per liter. This compositional difference influences their emissions of polluting gases.
CO2 Emissions
One of the main factors to consider in comparing these fuels is the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) they emit. Generally, diesel produces less CO2 per kilometer traveled compared to gasoline. This is because diesel has a higher energy efficiency. However, the ability of a diesel vehicle to cover a greater distance without producing as much CO2 can be detrimental when considering the total production of other pollutants.
Other Pollutants: NOx and Particulates
Besides CO2, diesel vehicles emit a higher amount of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and fine particulate matter compared to gasoline vehicles. These pollutants are responsible for health issues such as asthma and other respiratory diseases. On the other hand, gasoline tends to produce lower levels of NOx and particulates, although it still contributes to air pollution.
Impact on Health
Exposure to pollutants emitted by vehicles can have severe effects on public health. NOx and fine particulates are known carcinogens and are associated with a range of health problems, making diesel particularly harmful in this aspect. Especially in urban areas, where air quality is an increasingly concerning issue, understanding these effects is crucial.
Alternatives and Evolutions in the Industry
Recently, new technologies have emerged aiming to reduce the pollution emitted by both types of fuels. For example, some manufacturers have begun to restart the research and development of cleaner diesel engines, as mentioned in an article about the evolution of combustion engines in Europe. On the other hand, many companies are working on innovative solutions to reduce the environmental footprint of their operations, such as the use of technologies like Aeroshark in aeronautics.
Informal Conclusion
In summary, although diesel has advantages in terms of energy efficiency and lower CO2 production, its NOx and particulate emissions raise significant concerns about public health and the environment. It is crucial to continue researching and developing technologies that can mitigate the negative effects of both types of fuels. Global organizations and international collaborations are working on fuel reduction strategies and seeking cleaner alternatives, as mentioned here: international collaborations.
Comparison of Pollution: Diesel vs Gasoline
The question of which of the two fuels, diesel or gasoline, is more polluting has been the subject of intense debate in the environmental sphere. Both types of fuels have particular characteristics that determine their impact on the environment. Firstly, diesel, while known for its fuel efficiency and lower carbon dioxide emissions per kilometer traveled, generates higher levels of nitrogen oxides and fine particulates, which are harmful to human health and the climate.
On the other hand, gasoline tends to produce fewer solid particulates and nitrogen oxides, but emits more carbon dioxide compared to diesel. Despite this, gasoline produces a lower amount of pollutants on a local level, which can be an important factor in urban environments where air quality is a critical concern.
Furthermore, it is essential to consider the context in which these fuels are used. In terms of global impact, diesel may be more polluting due to its emissions of particulate matter and toxic gases, especially in older vehicles that lack advanced emission control systems. However, new technological advances in diesel engines are allowing for significant reductions in these emissions.
Finally, the choice between diesel and gasoline is not a simple matter. It involves considering user needs, environmental regulations, and applicable technology. With the growing awareness of climate change and urban pollution, the transition to cleaner alternatives, such as electric vehicles, is becoming increasingly important to mitigate the harmful effects of both fuels on the environment.