Aenergy saving: EU initiatives to reduce energy consumption

The energy saving has become a fundamental priority on the agenda of the European Union due to the growing need to combat climate change and reduce energy dependence. The initiatives implemented by the EU aim to establish ambitious targets that promote energy efficiency and encourage the use of renewable energies. Through various regulations and action plans, it seeks to significantly decrease energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, addressing current challenges and supporting a transition towards a more sustainable future.
Energy saving is a crucial challenge in the fight against climate change, and the European Union (EU) has implemented multiple initiatives to reduce energy consumption. These actions not only aim to decrease greenhouse gas emissions but also to promote energy efficiency, ensure sustainability, and achieve independence from fossil fuel imports. Through legislative measures and support programs, the EU focuses on transforming its energy model and creating a more sustainable future.
Energy efficiency in buildings
The building sector is responsible for 40% of total energy consumption and is at the heart of the EU’s strategy to improve energy efficiency. The new guidelines require that all public buildings be environmentally neutral by 2030, and that the public sector reduce its final energy consumption by 1.9% each year.
The updating of energy efficiency standards for buildings, which was backed by Parliament in March 2024, establishes that new constructions intended for public authorities must achieve zero-emission standards by 2028. This reform also prohibits subsidies for fossil fuel boilers starting in 2025.
Energy saving goals
The European Parliament adopted new targets in July 2023 that set a clear goal of reducing at least 11.7% of the overall energy consumption of the member states by 2030. To achieve these goals, each EU country must implement local and regional measures that translate into an annual saving of 1.5%. This measure will start with 1.3% until the end of 2025, progressively increasing to 1.9% by the end of 2030.
Promoting renewable energy
The EU has also made considerable efforts to foster the development of renewable energy. In December 2022, Parliament voted in favor of measures that require countries to issue permits for the installation of solar panels within one month. This contributes to the integration of clean energy into the energy system, thereby reducing dependence on fossil energy sources.
Additionally, standards have been established requiring new residential buildings to incorporate solar installations before 2030. These actions align with the European Green Deal and seek to promote a transition focused on sustainability.
Fighting energy poverty
A critical topic to consider in the context of energy saving is energy poverty. The new regulations being implemented include measures to support vulnerable households, ensuring that access to financing is available for those requiring assistance in the energy renovation of their homes. This is essential to combat the crisis of energy costs and invest in the well-being of the population.
Complementary measures for energy saving
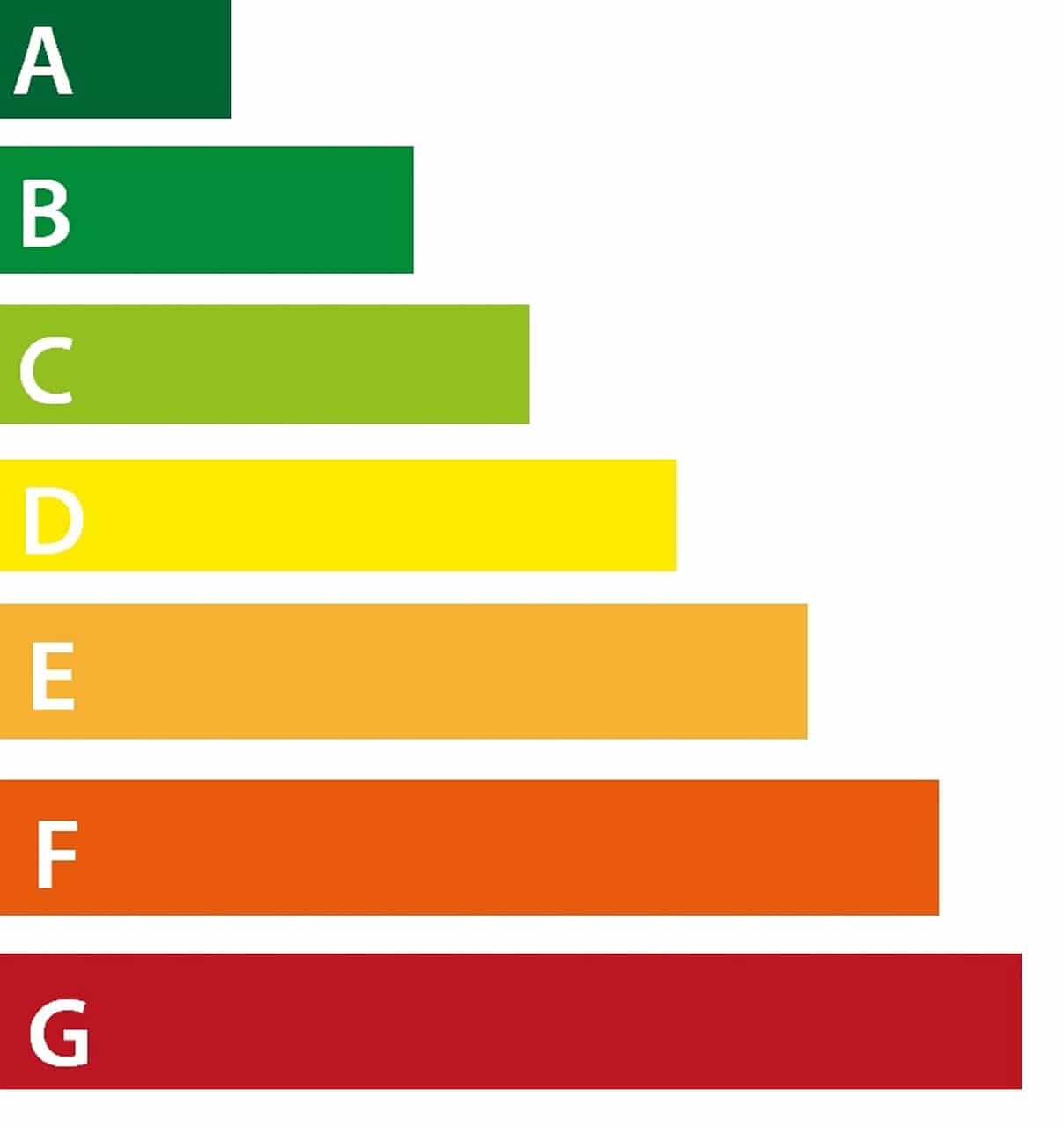
Efforts to reduce energy consumption also involve improving the efficiency of household appliances, where the EU has simplified energy labels. These labels are essential as they allow consumers to compare and choose products that have a lower impact on energy consumption.
Through various financing instruments, such as the Social Climate Fund and the RePowerEU Package, it aims to provide flexibility to member states, facilitating adaptation and investment in clean technologies to help the EU achieve its ambitious sustainability and energy saving goals.
Conclusions on energy saving in the EU
The EU’s initiatives for energy saving are fundamental not only to address the climate crisis but also to ensure a fair and sustainable transition towards a future with less dependence on fossil fuels. The implemented policies offer a clear framework to improve energy efficiency and promote a favorable investment environment towards cleaner and sustainable technologies.
Conclusion on Energy Saving in the EU
The initiatives of the European Union regarding energy saving are essential for effectively addressing climate change and the growing dependence on fossil fuels. Through a structured approach, the EU seeks not only to reduce energy consumption but also to foster sustainable development that benefits future generations.
The review of the energy efficiency legislation in 2018 and the adoption of new targets in 2023 reflect a strong commitment to a greener future. With specific goals for energy consumption reduction, the EU is preparing to tackle the enormous energy imports and greenhouse gas emissions, allowing for a transition to cleaner and renewable energy sources.
Moreover, the focus on modernizing buildings is crucial, as they represent a significant portion of energy consumption in the EU. The new regulations requiring the renovation of inefficient buildings and the implementation of renewable energy systems, such as solar energy, are important steps towards achieving effective reductions in carbon emissions and ensuring a healthier environment.
On the other hand, the fight against energy poverty highlights the importance of considering social equity within energy policies. Facilitating access to financing for vulnerable households will ensure that no one is left behind in the transition to energy efficiency and cost savings. The measures adopted by the EU are, therefore, a multifaceted attempt to address environmental, social, and economic issues comprehensively.